Conveyor transfer mechanism
Slider-Crank Mechanism
Introduction
This tutorial uses Conveyor transfer mechanism as an example to teach the kinematic and dynamic analysis using Solid Edge and Dynamic Designer.
|
|
|
|
Conveyor transfer mechanism |
Slider-Crank Mechanism |
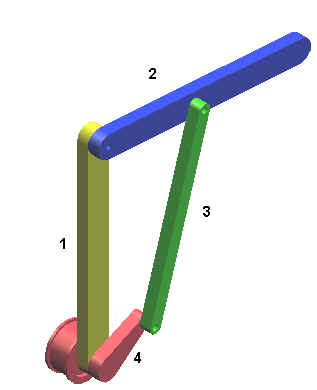
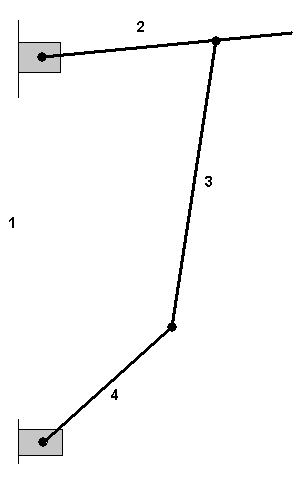
The mechanism used in this example is simple 4 bar Mechanism. A 4 bar Mechanism consists of four links with one being designated as frame (or ground). It is connected by four pin joints.
As designated in the figure, there are four links link 1, link 2, link 3 and link 4. Link 1 link 2 and link 3 all act similarly as connecting links. Link 1 is ground.
The following table summarizes the joints.
|
Joint Number |
Formed between links |
Joint type |
|
1 |
Link 4 and Link 1 |
Revolute (or Pin) |
|
2 |
Link 1 and Link 2 |
Revolute (or Pin) |
|
3 |
Link 2 and Link 3 |
Revolute (or Pin) |
|
4 |
Link 3 and Link 4 |
Revolute (or Pin) |
Degrees of Freedom: According to Gruebler’s equation,
![]()
where F = Degrees of Freedom (DOF)
n = total number of links in a mechanism
![]() = total number of primary joints (pins or sliders)
= total number of primary joints (pins or sliders)
![]() = total number of higher-order joints (cams or gears)
= total number of higher-order joints (cams or gears)
we have,
F = 3(4-1) – 2(4) – 0
= 9 – 8 - 0
= 1.
Hence, 4 bar mechanism has 1 DOF. In other words, 4 bar mechanisms are constrained or fully operated with one driver.
Click here to get the compressed (Solid Edge) part files.