I. Introduction
A.
The
History of Tires
The wheel is one of the greatest inventions
in human history due to its wide range of applications. These applications include any type of
transportation; whether it is people, materials, or equipment being moved. Charles Goodyear invented the first rubber
tires in 1839. Before the advent of
these tires, riding in a car was very uncomfortable due to the rough ride.
In 1830,
Goodyear wanted to develop a rubber product that was useable by the general
public. To carry out his experiments,
Goodyear bought a truckload of raw rubber from a shoe factory and attempted to
turn it into a complete solid. His
experiments were halted, when he was sent to prison for not paying his debt
from the rubber purchase 1.
This set back did not stop Goodyear.
While in debtor’s prison, Goodyear continued his experiments with the
raw rubber and when he was released from jail, the product he was making had
the consistency of gum. This rubber
material was called natural or India rubber. Goodyear did not stop there with his
experiments. He discovered that he was
able to harden the rubber by mixing the rubber with sulfur and then treating it
with an acid gas. The rubber ball was
tossed around and it accidentally landed on top of a hot stove. To the surprise of Goodyear, the rubber
began to change phase and melt, instead of scorching. However, when Goodyear attempted to scrape the rubber off the
stove, he discovered it had hardened to the consistency that he was trying to
achieve 1. With the
discovery of vulcanization, and the beginning of the industrial revolution in
both Europe and North America, the tire evolved from a rubberized canvas
protecting a rubber tube to a complex fabric, steel and elastomeric composition
21,22.
B.
Biography
of Charles Goodyear (1800-1860)

Goodyear
was born in New Haven, Connecticut on December 29, 1800. With no formal education, he
entered the hardware business
with his father as a partner in 1821 but later failed and was bankrupt in 1830. Thereafter he turned his talents to the
commercial improvement of India rubber, which, until his time was not used much
in industry because of the adhesiveness of the surface and because of its
inability to withstand temperature extremes 21. Goodyear began making rubber goods in the
fall of 1933, and the material sold for a fairly good price. Unfortunately, this rubber was not perfect. During the summer of 1934, the rubber melted
because of the heat and developed and offensive odor. Over twenty thousand dollars worth of products were returned to
him and the company 21.
Goodyear,
then went on to develop a nitric acid treatment to eliminate some of the rubber
defects and in 1837, he negotiated a contract in which he made mailbags for the
U.S. Government. The rubber fabric for
the mailbags was not much more successful and proved unsuitable at higher
temperatures. Goodyear later became
acquainted with Nathaniel Hayward, who was a foreman at a company called the
Eagle Company, where he had used sulfur in solvents to permeate the
rubber. The two men worked together and
made life preservers by the use of sulfurous acid gas and the solarizing
process which is the exposure of rubber sheeting to sulfur dioxide and then to
the sun’s rays. The next year, Goodyear
bought this patent from his partner 22.
Goodyear
continued his research for the means to make a better from of rubber without
the stickiness. He discovered that
rubber was charred and not melted by boiler sulfur. The famous vulcanizing process was discovered and was later
patented in 1844. Vulcanization was to
revolutionize the rubber industry.
Sadly, Goodyear was not much of a businessman and was unable to profit
financially from his discovery. He died
a poor man on July 1, 1860 and six of his twelve children also eventually died
from diseases brought on by the Goodyear family's persistent poverty. Charles Goodyear never saw a penny of the
earnings from Goodyear Tire & Rubber Co. since the company was formed
nearly 40 years after his death 21.
II. Tire Production
A.
Tire
Statistics
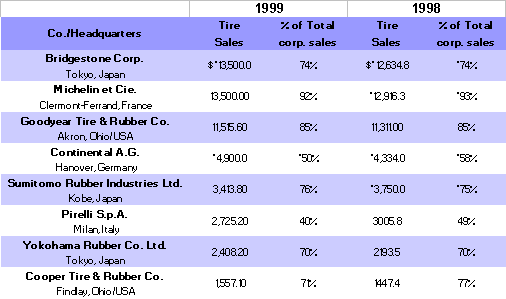
Some key tire production statistics for 1998-1999 are given in the following table 13,14:
B.
Raw
Materials
In order to manufacture a tire the major raw
materials required are: fabric (steel, polyester, nylon, or combinations
of these), rubber (synthetic and natural types: hundreds of different
types of polymers), reinforcing chemicals (carbon black, silica,
resins), anti-degradants (ozonants, paraffin waxes), adhesion
promoters (cobalt salts, brass on wire, resins on fabric), curatives
(cure accelerators, activators, sulfur), and processing oils (oils,
tackifiers, softners) 14,15.
C. Processing & Production
The tire making
process (see schematic below) starts by mixing different varieties of rubber
with process oils, carbon black, pigments, antioxidants, accelerators and other
additives, each of which contributes certain properties to the compound 13.
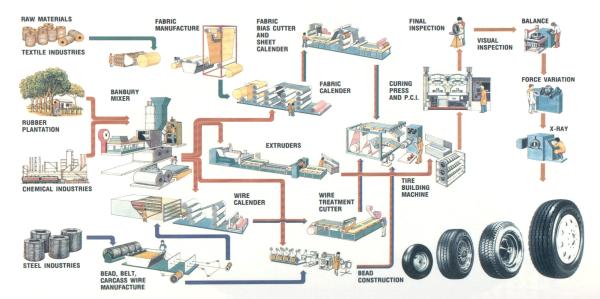
Figure 1: Schematic of the Tire Production Process
These ingredients
are mixed in giant blenders (called banbury mixers) under tremendous heat and
pressure. The ingredients are blended together into a hot, black gummy compound
that will be milled. The cooled rubber
takes several forms. Most often it is processed into carefully identified slabs
that will be transported to breakdown mills. These mills feed the rubber
between massive pairs of rollers, repeatedly feeding, mixing and blending to
prepare the different compounds for the feed mills, where they are slit into
strips and carried by conveyor belts to become sidewalls, treads or other parts
of the tire.
Still another
kind of rubber coats the fabric that will be used to make up the tire's
body. The fabrics come in huge rolls, and they are as specialized and critical
as the rubber blends. Many kinds of fabrics are used: (i.e. polyester or
nylon). Most of today’s passenger tires have polyester cord bodies.
Another component
called a bead, shaped like a hoop. It is made of high-tensile steel
wire, which will fit against the vehicle's wheel rim. The strands are aligned
into a ribbon coated with rubber for adhesion, then wound into loops that are
then wrapped together to secure them until they are assembled with the rest of
the tire.
Radial tires are
built on one or two tire machines. The tire starts with a double layer of
synthetic gum rubber called an inner liner that will seal in air and
make the tire tubeless. Next come two
layers of ply fabric, the cords. Two strips called apexes stiffen
the area just above the bead. Next, a pair of chafer strips is added, so
called because they resist chafing from the wheel rim when mounted on a
car. The tire building machine
pre-shapes radial tires into a form very close to their final dimension to make
sure the many components are in proper position before the tire goes into the
mold.
Now the tire
builder adds the steel belts that resist punctures and hold the tread
firmly against the road. The tread is the last part to go on the tire. After
automatic rollers press all the parts firmly together, the radial tire, now
called a green tire, is ready for inspection and curing.
The curing
press is where tires get their final shape and tread pattern. Hot molds shape
and vulcanize the tire. The molds are engraved with the tread pattern,
the sidewall markings of the manufacturer and those required by law. Tires
are cured at about 300 oF for 12 to 25 minutes, depending on their
size. The tires are popped from their molds and taken to final finish and
inspection. If anything is wrong with the tire, it should be rejected. An inspector’s trained eyes and hands catch
some flaws; specialized machines find others 14, 15, 17.
Some tires are
pulled from the production line and X-rayed to detect any hidden
weaknesses or internal failures. Also, quality control engineers regularly cut
apart randomly chosen tires and study every detail of their construction that
affects performance, ride or safety 17.
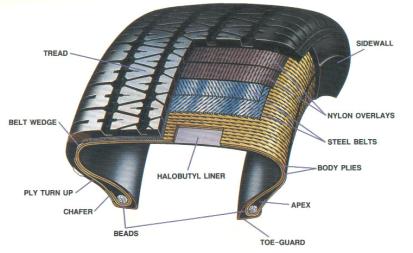
Figure 2: Cross-Section
D.
The
Chemistry of Tires
Introduction
Vulcanization, or the process by which rubber is heated with sulfur to create a network of chemical cross-links, was invented by Charles Goodyear in 1839. It produces a finished product that is not sticky like raw rubber, does not harden with cold or soften much except with great heat, is elastic, springing back into shape when deformed instead of remaining deformed as unvulcanized rubber does, is highly resistant to abrasion. The process, a key advancement during its time, has been refined and enhanced since 2.
Natural rubber, also known as isoprene, when
vulcanized will form a three dimensional network of mono-, di-, and polysulfide
bridges which give the rubber its characteristic strength and elasticity. It is
also important to note that the cross-links that give the tires these
properties are not just sulfide linkages.
They can be ionic clusters, polyvalent organic clusters, or polyvalent
metallic ions. The process increases retractile force of the material, while
decreasing the amount of permanent deformation occurring with the removal of a
load 2.
The other major chemical process associated
with tire manufacturing is the process by which brass is coated onto the steel
belts, which are used in tire reinforcement.
The brass coating adheres better to the rubber, and also helps to
increase the retractile force of the composite material 1, 2.
Vulcanization
The process of vulcanization profoundly
changes the molecular structure of rubber, with the average distance, in terms
of molecular weight, between linkages being approximately 4000-10000. Hard
rubber is vulcanized rubber in which 30 – 50 % sulfur has been mixed before
heating; soft rubber contains usually less than 5 % sulfur. After the sulfur
and rubber (and usually an organic accelerator) are mixed, the compound is usually
placed in a mold and subjected to heat and extreme pressure A vulcanized
material cannot be processed in an extruder, mixer, or any device, which
requires the material to flow.
Therefore, the vulcanization is done after the material has taken its final
shape or form 1,14.
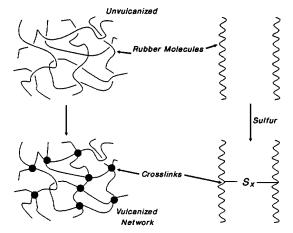
Figure
3: Sulfide
Network Formation
The characterization of polymers
starts with certain properties such as hysteresis, tear strength and tensile
strength all of which can be plotted as a function of cross-link density within
the polymer. This is shown in the
figure below:
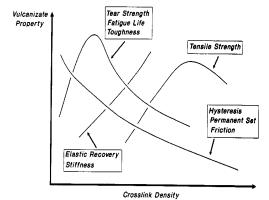
Figure
4: Vulcanizate Properties as Function of Cross Link
Density
Hysteresis represents the history
dependence of physical systems. If you push on something, it will yield: when
you release, does it spring back completely? If it does not, it is exhibiting
hysteresis, in some sense. In the
figure above, hysteresis decreases with increasing cross-links. This is because the cross-links give the
material some strength and rigidity, which allow it to return to its original
shape when the loading is relieved. A
material with no cross-links would remain permanently deformed 2.
There exist many types of vulcanization:
with and without accelerator, phenolic curatives, benzoquinone derivatives,
metal oxide, organic peroxide, and dynamic.
This report will focus mainly on the chemistry of vulcanization with and
without accelerators 2.
Vulcanization without the use of an
accelerator was commonplace until 1906 when Oenslager found the first useful
accelerator (aniline) for use in the process.
The unaccelerated process utilized elemental sulfur at 8 parts per 100
parts of rubber (phr) and required a temperature of 140 oC for 5
hours. The common reaction mechanism
for unaccelerated vulcanization is the free-radical method, given below 1,2:
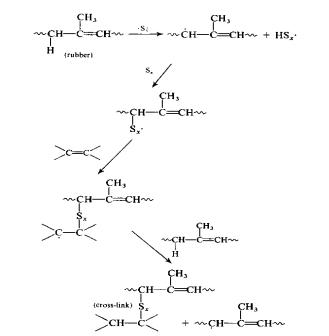
Figure
5:
Unacclerated Vulcanization Mechanism via Free-Radical Polymerization
The reaction is a basic free-radical
polymerization between isoprene and a sulfur radical. Since this scheme has a long curing time, it is not practical for
use in designing a mass-production plant around. As discussed in the next section, accelerators can greatly
increase the rate of reaction (hence, the name accelerator) and thus
unaccelerated vulcanization is generally not used except for certain specialty
products.
Accelerated vulcanization, however,
can perform the same operation listed above at the same temperature with an
elemental sulfur concentration of 0.5 phr and decrease the reaction time to as
low as 1 to 3 minutes 2. The
main mechanism for accelerated vulcanization is listed below:
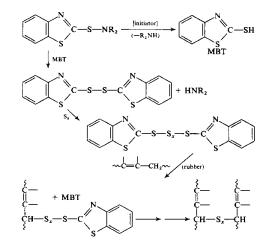
Figure
6: Mechanism
for Accelerated Vulcanization
Where MBT (2-Mercaptobenzothiazole) is the
accelerator for the reaction. MBT acts
as an initiator by removing the –R-NH2 group from the material allowing
it to react with itself quicker. A list
of common accelerators is given in the figure below. The most important of which is MBT, which replaced the toxic
aniline in 1925. MBT reacts as shown
above with the sulfur, thus allowing it to react even faster with the rubber
than the elemental sulfur 1.
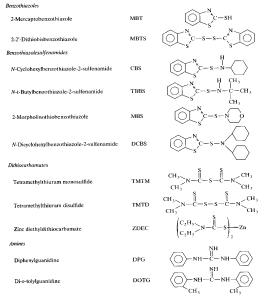
Figure
7: Different
Types of Accelerators for Vulcanization
The accelerators given above can be
used in a variety of roles to either increase the rate of linkage formation, or
the extent of formation (di-, tri-, poly-linkages, etc.).
Brass Wire
Adhesion
The second area of importance is the
brass-coating placed on steel belts for adhesion to the melted rubber. Since carbon steel has a poor affinity for
vulcanized rubber, the overall strength of the tire is reduced. Therefore, brass (CuZn) is deposited on the
surface of the steel belts so that a stronger bond between the steel and rubber
can be formed. As the rubber flows
around the steel belts in the mold, a thin copper sulfide (CuS) layer is formed
on the surface of the steel belts.
Since the layer is porous, the rubber begins to move into the
layer. When the vulcanization process
is started, the rubber forms cross-links not only with itself, but with the CuS
also, resulting in very strong attractions.
The entanglements between the rubber and CuS layer help form a powerful
bond between the rubber and steel. This
process is diagramed below 1, 2:
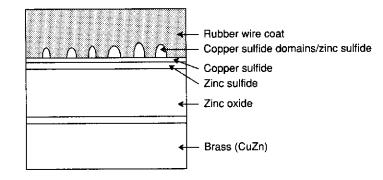
The formation of these domains
creates a considerable adhesive force between the 2 materials, and is necessary
for the long-term durability and strength of the material. A problem with this process is that the
presence of either zinc/iron sulfides (ZnS/FeS) will inhibit the process. Neither of these materials exhibits the
porosity that CuS does, therefore the entanglements that form the strong bonds
do not occur, resulting in weak surface adhesion. Also, the presence of Zn2+ will corrode the rubber
because it will form either ZnO or ZnOH will accumulate in the CuS layer and
will displace the disulfide linkages.
This can be prevented by doping the brass with small amounts of
trivalent cobalt 1, 2.
E.
Disposal
and Recycling of Used Tires
Today, a variety of recycling
techniques encourage the use of tires at the end of their lifetime. They can be
used for energy production as a fuel, especially in cement works. Or the
materials can be re-used, for example by transforming the tire into a powder
which is used for flooring materials, for making rubber objects or in the
manufacture of new tires 13, 12.
Some
statistics on tire recycling are given below.
These statistics are for retreaded-tire usage in 2000 11:
- ~ 27.7
million retreaded tires were sold in North America in 1999
- ~ 600
million lbs. of tread rubber used (recycled) by the North American retread
industry
- Almost all
of the world’s commercial airlines use retreaded tires
- Cost of a
retreaded tire is ~ 30-50 % lower than that of a new tire, with same
performance
- Retreading
conserves millions of gallons of oil each year (each new passenger tire
made from 7 gallons of oil vs. 2 gallons for a retreaded tire)
III. Tread Separation Problem Overview
A.
Suspicion
of a Problem
The safety of sport utility vehicles has
always been an issue for the general public.
Complaints include: excessive gasoline consumption, and overbearing size
of the vehicles on the road. In late
July 2000, authorities noticed that sports utility vehicles had a tendency to
tip over, and this observation was especially prevalent in regard to the Ford
Explorer models. The initial
explanation many came up with was that the vehicles were too large and that
their center of gravity was higher compared to other SUV’s. After further investigation from the
National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA), the agency
noticed that all rollover accidents involving the ford explorer had one thing
in common; they all had the same tires.
The tires that were used on those vehicles were the Firestone ATX, ATX
II and Wilderness AT tires. The agency
also noticed that in most of the accidents, the tires were damaged in such a
way that the tread was completely separated from the radial 3,7.
B.
Cause
of Problem
After several months of investigation, which involved cutting apart over 850 tires and examining more than 2,500 recalled tires; the Bridgestone/Firestone Corporation believed that they had an idea as to what was going wrong. The tire manufacturers believed that there were four major factors that resulted in the increased rate of accidents 4, 5:
1. The Ford Motor Company
2. The drivers of the vehicle(s)
3. The tread design
4. The adhesiveness to the steel belts
Bridgestone/Firestone admitted that part of
the problem was due to their design, but the company also blamed the Ford Motor
Company, as well as the drivers for the accidents. Since most of the tires were installed as original equipment on
Ford Explorers, Bridgestone/Firestone asserted that Ford designed and built the
vehicles too heavy for the tires. Also,
Bridgestone/Firestone claimed that the tire pressure recommended by Ford, 26
psi, was too low and that the recommended tire pressure should have been
approximately 30 to 35 psi. Ford
maintains that their vehicles were properly designed, and do not in any way,
contribute to the tire tread separation 4,8.
Bridgestone/Firestone believed that the
second factor contributing to the failure of the tires was inadequate consumer
maintenance. They stated that the tires
should have been accurately inflated, which would have reduced the possibility
of the tire heating-up, therefore preventing the tread separation.
Finally, investigators found that there was a problem with the tread design in the ATX tires. The problem with the tread design involved the shoulder pocket of the tire, which is the interface between the wall of the tire and the tread. The poor design of the tread caused the tires to prematurely, and more profoundly than other tires. However, the tread design was not the only design problem with the tires. Problems with the rubber adhesion to the steel belts also were a cursory cause of the tread separation. This problem was confined to the tires that were made and manufactured in the plant in Decatur, Illinois 7.
C.
‘Weak
Link’ in Tires
Although there are many causes as to why the
treads separated, the main cause for the accidents was the design of the tire
itself. With the added stress and other
factors to the tires, the design was not able to withstand the actual
conditions. Tire
manufacturers know that a leading cause of tread separation is due to the
design and placements of the belts and overlying tread. Also, tread and belt separations can occur
due to poor adhesion of the components from the use of old and
expired adhesives, improper temperatures, rust, unclean manufacturing
facility, moisture, oxidation, grease, and particulate matter. Many former and current employees of the
Decatur Firestone plant have told reporters and/or lawyers about how poor the
quality control is at that plant. Joe
Roundtree, a former employee of Firestone told Dateline News that, “there were
times when rubber, which had been tagged as rejected earlier in the day would
be used anyways when supplies ran short”.
Roundtree also noted that a tool called an awl (used for a variety of
jobs, often in the early stages of construction, to release pockets of air
trapped in between layers of the tires) was being used in the post-processing
of the tires. Also, other employees
from the Decatur plant have testified that Firestone told their employees to
puncture bubbles in order to cover flaws and also the poor quality control in
the keeping of steel-belts 9.
Of
all of the known problems resulting in tire tread and belt separation, the
leading cause of tread separation is the poor adhesion between the rubber and
the steel. The method used most often
involves plating the metal with brass and to apply a rubber
compound containing sulfur. If the sulfur and other compounds are not
to the correct mixture, then incomplete adhesion occurs. Also if the
brass plating is allowed to oxidize, then adhesion will not occur
properly. If there was a luster to the
belts, then most probably they were not properly coated with brass, or properly
kept 11.
Another
well know design defect, is not including an extra nylon cap belt to
encapsulate the underlying belts and bond them to the outer
core. This nylon cap belt is
placed between the top belt and the outside tire tread, therefore in a sense
capping the inner belts to the outer core to prevent the spread or
movement to the belt edge. This extra
belt was a missing
component in the Firestone ATX, Firestone ATX II and the most of the Wilderness
AT tires subject to the Firestone recall.
Had Firestone elected to use this extra cap belt, many experts believe
the numbers of tread separations would have been dramatically reduced. Firestone
had no legitimate excuse for excluding this important safety feature.
IV. Lawsuit Against Firestone and Ford Motor Co.
A.
Litigation
Pending
Both Firestone and Ford are in an ongoing battle with the public, both in terms of litigation and reputation. Many who have been in an accident or lost a family member due to a tread separation and/or rollover, have filed individual and class action lawsuits against Ford and Firestone. Thus far, most of the cases have been settled out of court and a class action lawsuit remains. One of the first major lawsuits brought against Firestone ended up in a favorable judgment for the plaintiff -- 90 million dollars in damages 8.
B.
Firestone’s
Position on the Issue
Bridgestone/Firestone have taken responsibility for the faulty
design in their tires. They have
initiated a worldwide recall of the faulty tires and have offered their
customers new tires, free of charge, to replace the defective ones. Firestone has also gone ahead and began to
test their other tires for the same problem, and modify any that require doing
so. Although Firestone has acknowledged
the mistakes in their design, they do not believe that the blame should be
placed wholly on them. They believe
that the design parameters of SUV’s (such as the height and size of the
vehicle) and the drivers/driving conditions are to blame for this unfortunate
tragedy 13, 18.
C.
Ford
Motor Corporation’s Position
Ford Motor Corporation, still vehemently stands by the design of their Explorer series SUV’s, and deny any accusations that blame them for the accidents. Their argument has recently been bolstered, as a jury in Texas found the company not responsible for a rollover that occurred in a Ford Explorer. The company, however, has stated that they will investigate their recommendation of 26 psi versus the Firestone recommended 30-35 psi 9, 3.
D.
Plaintiff’s
Position on Issue
Many of the victims have filed lawsuits against both companies to settle for appropriate damages in their respective cases. The main action of the plaintiff’s and their supporters for the moment has been a boycott of both Ford and Firestone products. The boycott of Firestone has had a much more profound impact on Firestone than Ford, with Ford still maintaining sales of their other top selling vehicles. Firestone, on the other hand, is suffering one of their biggest losses in company history and may be forced out of business within a year, according to some analysts 5.
V. Conclusion
At first glance, one might blame the
Bridgestone/Firestone Corporation for the tread separations in their tires
since they manufactured the defective tires.
But further investigations show that the tire manufacturing company is
just one of many factors that could have potentially prevented this from
happening. No significant person, or
company is at blame at this moment as further investigations continue. While investigations continue, lawsuits
pending are finally brought to an end with settlements settle out of
court. A mistake, simple, yet
correctable, has caused Firestone to pay millions in damages to the victims and
could cause the shut of the company.
Works Cited
1.
Alliger, G. et. al. Vulcanization of Elastomers –
Principles and Practice of Vulcanization of Commercial Rubbers. Reinhold Publishing; New York, NY: 1964.
2.
Mark, James E. et. al. Science
and Technology of Rubber – Second Edition. Academic Press; San Diego, CA:
1994.
Specific Websites:
3. Reuters: http://www.cnn.com/2001/WORLD/asiapcf/east/02/22/japan.bridgestone/index.html
4. Candiotti, Susan: http://www.cnn.com/2001/LAW/01/08/firestone.settlement.bus.01/index.html
5. Candiotti, Susan: http://www.cnn.com/2001/LAW/01/08/firestone.01/index.html
6. Garsten, Edward: http://www.cnn.com/2000/US/12/21/firestone.nhtsa/index.html
7. Candiotti, Susan: http://www.cnn.com/2000/LAW/10/27/firestone.depositions.bus/index.html
8.
AP: http://cnnfn.cnn.com/2000/09/11/companies/bridgestone/
9. AP:
http://www.msnbc.com/news/484123.asp
10. N/A: http://www.michelin-us.com/us/eng/tire/guide/index.html
11.
N/A: http://www.itra.com/ind_info.html
12. Rubber Manufacturers Association: http://www.rma.org/publications/pdf/mis_demo_mtr.pdf
13.
http://www.rubbernews.com/subscriber/charts/global.html
14. http://www.goodyear.com/us/products.html
15. http://www.bridgestone-firestone.com
16. http://www.nhsta.dot.gov/hot/firestone/indes.html
17. http://www.howstuffworks/com/tire1.htm
19. http://www.firestone-tire-recall.com
20. http://www.tire-defects.com/Default.htm
21.
http://www.invent.org/book/book-text/47.html
22. http://www.goodyear.com/us/corporate/strange.html